I’ve already shown how you can add the mercurial revision into the version automatically with native C/C++. However, there are some extra hurdles you have to jump to make this work for .NET. The problem is that you can’t use static variables or class data in the assembly attributes – you have to use constant literals or expressions. As a result, we can’t just generate a simple class and reference it in the AssemblyAttributes.
Again I’ll be building on the previous posts and discussing how to do this with Visual Studio 2010 Professional and Mercurial using TortoiseHg, this time for a .NET application. Other versions of Visual Studio should work similarly and other Mercurial packages will work as well, as long as they provide command-line tools that are in the path of your IDE. We’ll be using a GlobalAssemblyInfo file to share common assembly attributes across projects in the same solution as discussed here.
The source code for this post is available here.
Step 1: Add a Version Project
Although I didn’t do this for the native solution, I find adding a specific Version project to the solution is beneficial. The reason is that we are generating common version info to be used across the entire solution, however the first project in the build order needs to be the one to generate this info. Depending on your project dependencies there may not be an obvious or good place to do this. By adding a Version project and making all other projects depend on it we have an easy place to generate the necessary files.
- Add a project named Version to your Solution
- Add a reference to Version from all the other projects in your Solution
Step 2: Add a GlobalAssemblyInfo Template
Rather than generate the entire contents of the GlobalAssemblyInfo.cs file in the script, where it’s harder to find and edit when needed, we’ll use a template. Create a file named GlobalAssemblyInfo.cs.tmpl in the Properties folder of the Version project. Copy the code below into the template and make any desired customizations to match your environment.
Notice the $REVISION$, $CHANGESET$ and $LOCAL_MODIFICATIONS$ tokens. We’ll use these to place the necessary Mercurial information in the file we generate.
// This file contains common AssemblyVersion data to be shared across all projects in this solution.
using System.Reflection;
[assembly: AssemblyCompany("Zach Burlingame")]
[assembly: AssemblyProduct("DotNetHgAutoVersion")]
[assembly: AssemblyCopyright("Copyright © Zach Burlingame 2011")]
[assembly: AssemblyTrademark("")]
[assembly: AssemblyCulture("")]
#if DEBUG
[assembly: AssemblyConfiguration("Debug")]
#else
[assembly: AssemblyConfiguration("Release")]
#endif
// Version information for an assembly consists of the following four values:
//
// Major Version
// Minor Version
// Revision
// Build
[assembly: AssemblyVersion("1.0.0.$REVISION$")]
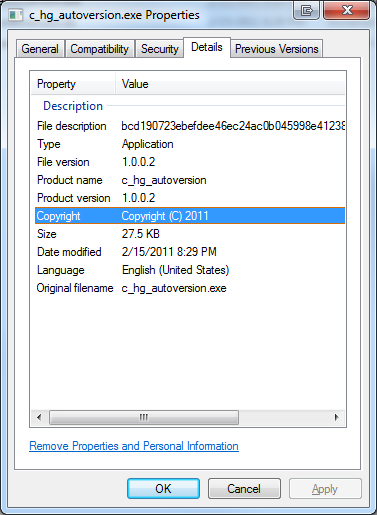
[assembly: AssemblyTitle("$CHANGESET$$LOCAL_MODIFICATIONS$")] // This is visible as the "File Description" on the Details tab of the Explorer pane
Step 3: Using WSH to Generate Global Assembly
Next we need to add a file to our Version project named hg_version.jse. Personally, I like to add this file under the Properties filter of my project. Copy the code below in to the script file. This code does two things:
- Creates GlobalAssemblyInfo.cs
- Extracts the desired Mercurial version info from the working copy and places it in the header
The extracted version info includes the full node identity, the revision number and if there are any local modifications to the working copy. Note that in counter-intuitive fashion, the AssemblyTitle attribute is what sets the Description field when viewed from the Details tab of the Properties pane in Explorer. Meanwhile the AssemblyDescription field isn’t displayed at all and rather is only accessible through API calls against the binary. Why MS did this, I do not know…
var fso = new ActiveXObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject");
var shell = new ActiveXObject("WScript.Shell");
var ForReading = 1, ForWriting = 2, ForAppending = 8;
var projectDir = "../../";
var hgRevNum = shell.Exec("hg identify --num");
var rev = hgRevNum.StdOut.ReadAll();
var hg_revision = String(rev).replace(/\n/g,"").replace(/\+/g,"");
var hg_local_modifications = '';
if( String(rev).replace(/\n/g, "").indexOf("+") != -1 )
{
hg_local_modifications = '+';
}
var hgChangeset = shell.Exec("hg parents --template \"{node}\"");
var changeset = hgChangeset.StdOut.ReadAll();
var hg_changeset = String(changeset).replace(/\n/g,"");
var hgChangesetShort = shell.Exec("hg parents --template \"{node|short}\"");
var changeset_short = hgChangesetShort.StdOut.ReadAll();
var hg_changeset_short = String(changeset_short).replace(/\n/g,"");
var tmplFile = fso.OpenTextFile( projectDir + 'Properties/GlobalAssemblyInfo.cs.tmpl', ForReading, false );
var strContents = tmplFile.ReadAll();
tmplFile.Close();
strContents = String(strContents).replace(/\$REVISION\$/g, hg_revision );
strContents = String(strContents).replace(/\$LOCAL_MODIFICATIONS\$/g, hg_local_modifications );
strContents = String(strContents).replace(/\$CHANGESET\$/g, hg_changeset );
strContents = String(strContents).replace(/\$SHORT_CHANGESET\$/g, hg_changeset_short )
var asmFile = fso.CreateTextFile( projectDir + '../GlobalAssemblyInfo.cs', ForWriting, true );
asmFile.Write( strContents );
asmFile.Close();
Step 4: Add a Pre-build Event
Add a pre-build event to the Version project to call the hg_version.jse script and generate GlobalAssemblyInfo.cs.
- Right-click on the Version project
- Select Properties
- Select the Build Events tab
- In the Pre-build event command line box, enter:
cscript.exe “$(ProjectDir)\Properties\hg_version.jse”
Step 5: Add a link to the GlobalAssemblyInfo.cs file in each project
- In Visual Studio, right-click on a project
- Select Add->Existing Item
- Browse to GlobalAssemblyInfo.cs
- Select the file
- Click the drop-down arrow next to Add and select Add As Link
- Move the link to your Properties folder (optional, but keeps things neat)
Step 6: Update the AssemblyInfo.cs for each project
In order to avoid duplicate annotations for assembly information, you must remove entries from the AssemblyInfo.cs file that appear in the GlobalAssemblyInfo.cs file. In our example here, this is what we end up with:
using System.Reflection;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
// General Information about an assembly is controlled through the following
// set of attributes. Change these attribute values to modify the information
// associated with an assembly.
[assembly: AssemblyDescription("")] // This is not visible on the Details tab of the Explorer pane
// Setting ComVisible to false makes the types in this assembly not visible
// to COM components. If you need to access a type in this assembly from
// COM, set the ComVisible attribute to true on that type.
[assembly: ComVisible(false)]
// The following GUID is for the ID of the typelib if this project is exposed to COM
[assembly: Guid("dad09178-814d-43f4-b76d-0fbe29a32544")]
Conclusion
And there you have it! Now when you build your solution, all your project assemblies will have the latest Mercurial version information included in their meta-data automatically.
Other Posts in this Series
- Mapping Binaries in the Field to Source Code in the Repository
- Versioning a Native C/C++ Binary with Visual Studio
- Versioning a .NET Assembly with Visual Studio
- Integrating the Mercurial Revision into the Version Automatically with Native C/C++
- Integrating the Mercurial Revision into the Version Automatically with .NET
- Integrating the Subversion Revision into the Version Automatically with Native C/C++
- Integrating the Subversion Revision into the Version Automatically with .NET